Budapest System – The International Microorganism Deposit System
Facilitating the protection of biotechnological inventions
The Budapest System provides a practical mechanism when pursuing patent protection of inventions involving biological material in a large number of countries.
The premise of the mechanism is the recognition of a single deposit of a microorganism with an international depositary authority throughout the countries that are parties to the system. In practice, the international deposit system established by the Budapest Treaty has been used for the deposit of not only microorganisms, but for other biological materials, including cells, tissue culture, fungi or plasmids.
A Contracting State of the Budapest Treaty must recognize, for the purposes of patent procedure, the deposit of a microorganism with any "international depositary authority" (IDA), irrespective of whether such authority is within or outside the territory of the said State. Such recognition includes the recognition of the fact and date of the deposit with the IDA and that a sample furnished by the IDA is indeed a sample of the deposited microorganism. In addition to Contracting States, some regional patent organizations (ARIPO, EAPO, EPO and OAPI) recognize the effect of the Budapest Treaty for the purpose of their patent procedures.
Sufficient disclosure of the invention is a requirement for the grant of patents. Normally, an invention is disclosed in writing by means of a description and drawings. Where an invention involves biological material or the use of it, a description alone or with drawings may not be enough for a person skilled in the art to carry out the claimed invention. Accordingly, a deposit of the biological material with an authorized institution supplements the description and provides a practical means to meet the sufficiency of disclosure requirement in many countries.
Once a biological material is deposited with an IDA for the purposes of the patent procedure, the IDA shall store the biological material in a manner that it is kept viable and uncontaminated. It is also a task of the IDA to provide samples of the deposited biological material to interested parties, in accordance with the Regulations under the Budapest Treaty and national law. Availability of samples of the deposited biological material is important for the proper functioning of the disclosure mechanism under patent law.
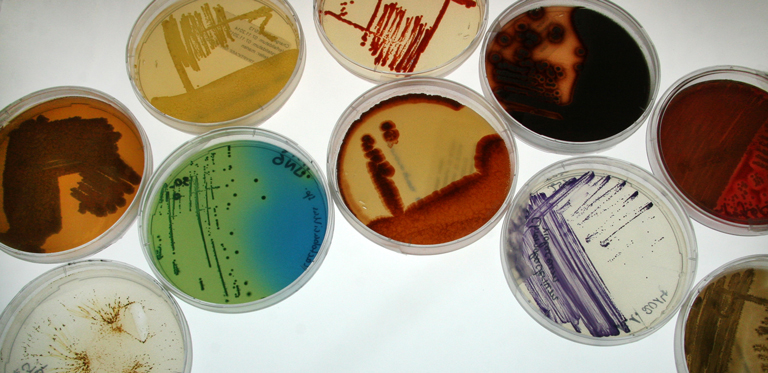
The Budapest Treaty offers applicants an efficient and cost-effective means of meeting the disclosure requirements associated with patenting microorganisms. (Photo: DMSZ)
Benefits of the Budapest System
By acknowledging the multiple legal effect of a single deposit, the Treaty makes the patent procedure simpler and patenting more attractive in the States party to the Treaty.
Global
A single deposit of a biological material with any of the IDAs is recognized in a large number of countries as part of the patent disclosure requirement.
Streamlined
Patent users benefit from a streamlined procedure of deposit and storing of biological material as well as furnishing of samples of deposited biological material.
Economical
Patent applicants save money by only one deposit of biological material with any of the IDAs that is recognized by all Contracting States and regional organizations.
One-stop-shop
Deposited biological materials are managed by one IDA that processes it and makes it available to authorized parties under certain conditions.
News
-
Accession of Brazil to the Budapest Treaty
October 20, 2025
-
2024 Statistics on Deposits of Microorganisms Now Available
September 2, 2025
International depositary authorities
An international depositary authority (IDA) is a scientific institution, typically a culture collection, that is capable of storing biological materials. IDAs are designated by the contracting States and must meet specific requirements set by the Budapest Treaty to ensure proper handling, storage, and distribution of deposited biological materials.
How to become an international depositary institution?
Article 6(2) of the Budapest Treaty and Rule 2 of the Regulations under the Budapest Treaty provide the detailed requirements that a depositary institution must comply with to qualify for the status of IDA.
A depositary institution that complies with the conditions to apply for the status of IDA must be formally nominated by the Contracting State in which it is located to acquire the status of IDA. Article 7 and Rule 3 of the Budapest Treaty and its Regulations regulate the procedures for the acquisition of the status of IDA.
Find an international depositary authority
Budapest System resources
Legal resources
The Guide contains information on the procedures and requirements concerning the deposit of microorganisms provided for under the Budapest Treaty, including:
- Model forms
- Requirements and Practices of IDAs regarding the deposit and furnishing of samples under the Budapest Treaty (Section D)
- Requirements and Practices of IP Offices of State Party to the Budapest Treaty and Regional patent organizations regarding the deposit of microorganisms for the purposes of patent procedure (Section E)
Statistics
Number of deposits/samples furnished under Rule 11 of the Regulations of the Budapest Treaty – based on information provided to the International Bureau of WIPO by international depositary authorities [XLSX]
Questions about the Budapest System?
Our team is available to answer all your questions and assist you.
