World Intellectual Property Report 2022
The Direction of Innovation
World Intellectual Property Report 2022
World Intellectual Property Report 2022
The Direction of Innovation
The 2022 edition of the World Intellectual Property Report examines how crises such as pandemics and wars can influence the evolution of innovation by looking at historical scientific and technological advances from vaccine development during the COVID-19 outbreak to the rise and prevalence of digital technologies of today.
The report also highlights how policymakers can drive innovation in a direction that best responds to societies’ needs to address the grand challenges of climate change and health.
How will technology change in the future?
As we enter the third decade of the 21st century, new and powerful factors influence the direction that innovation is taking in science, technology and medicine to address the grand challenges of today. Most recently, the COVID-19 pandemic, climate change and the digital revolution have been major factors of technological and scientific change.
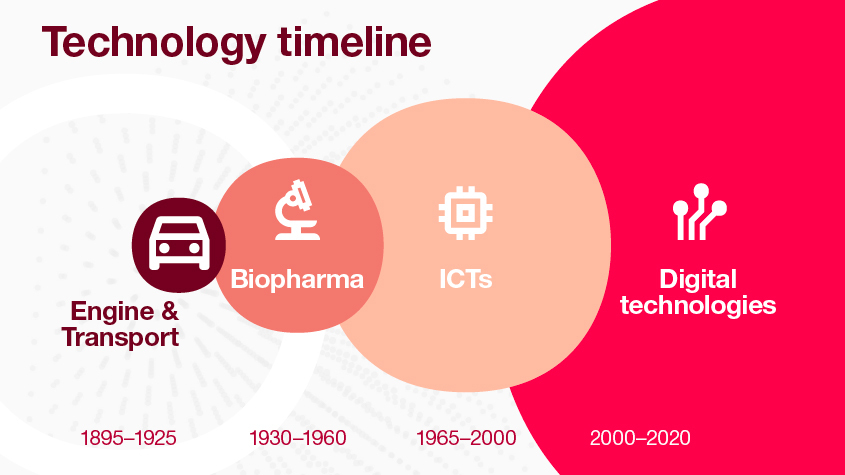
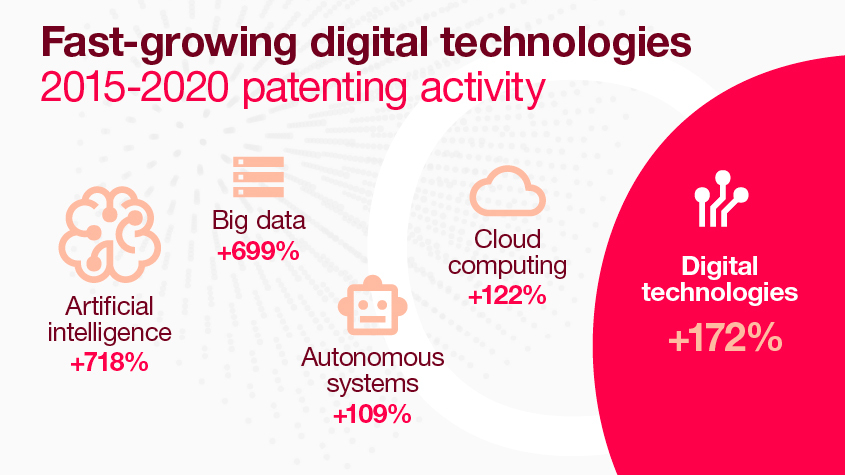
Digital transformation heralds the Fourth Industrial Revolution
The 21st century has seen digital technologies taking the world by storm, with some economists billing this as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, a fully-data driven economy. Digital general-purpose technologies are expected to make strides in optimizing transportation systems, transforming medical research and healthcare, and improving access to education.
Read our report to find out more about how digitalization is changing the world [PDF]
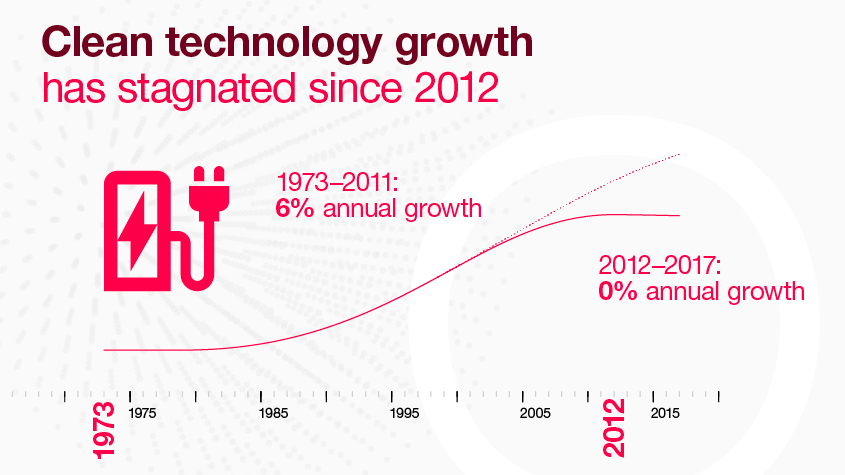
Green technology to tackle climate change
Fighting climate change has become a priority at the top of policy agendas around the world. Clean technology growth has stagnated in the past decade. Reaching ambitious carbon emission-reduction targets will depend on the adoption of innovative technologies. Policy measures and public funding will increasingly prioritize investments in new technologies.
Read our report for more information on the need to address climate change [PDF]
Crisis-driven innovations
In a sudden crisis such as a natural disaster, war or a disease outbreak, governments can play a decisive role by mobilizing forces, redirecting funding and coordinating the efforts of the public and private sectors.
Innovation during the pandemic
COVID-19 generated and accelerated demand for new technologies with which to curb the spread of the virus and treat infection. The scientific and technological community developed, with significant government funding, a range of vaccines in record time.
Read our report to find out more about the lessons learnt from the COVID-19 pandemic [PDF]
Innovation as a consequence of war
Treating wounded soldiers during the Second World War required new technological solutions. The US government reacted by increasing its R&D budget 100 times, allowing for numerous medical breakthroughs to occur. These opened avenues for further research and medical improvements that reached far into the future.
Read our report to find out more about the lessons learnt from World War II [PDF]

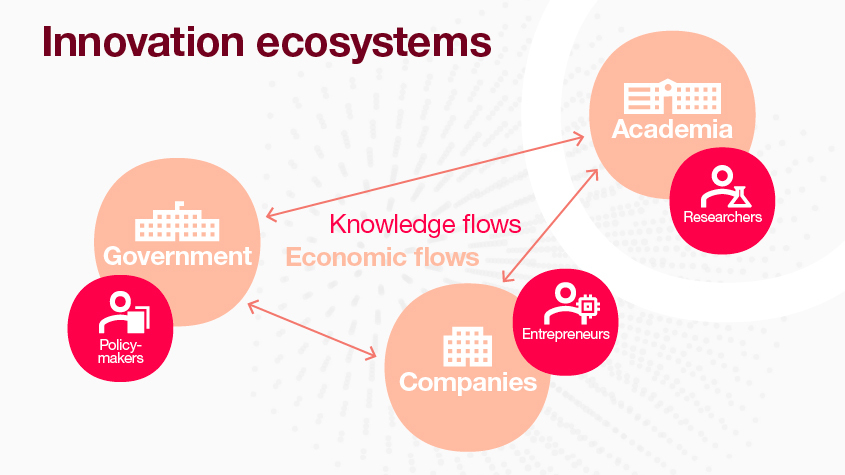
How the innovation ecosystem sparks new technologies
An innovation ecosystem can be defined as the combination of all the stakeholders that make choices influencing innovation-related outcomes and, consequently, the direction of innovation. The choices and interactions that occur within the ecosystem are paramount and based on two elements:
1. Knowledge flows
Knowledge flows define the interaction between innovation ecosystem stakeholders. They provide potential innovation opportunities available to stakeholders, which in turn set the direction of innovation.
2. Economic flows
Based on predictions, companies, entrepreneurs and governments identify innovation opportunities that may potentially generate private and social returns – that is, the potential profit to a company or society.
Read our report to find out more about interactions within innovation ecosystems [PDF]
About the World Intellectual Property Report
The World Intellectual Property Report, published every two years, offers fresh insights into the role of innovation in market economies and, in doing so, fosters evidence-based policy-making. Each edition focuses on specific trends in an area of intellectual property (IP).
