WIPO Develops Cutting-Edge Translation Tool For Patent Documents
Geneva,
October 31, 2016
PR/2016/799
The World Intellectual Property Organization has developed a ground-breaking new “artificial intelligence”-based translation tool for patent documents, handing innovators around the world the highest-quality service yet available for accessing information on new technologies.
- Video: DG Gurry on WIPO Translate Video
- Watch on YouTube
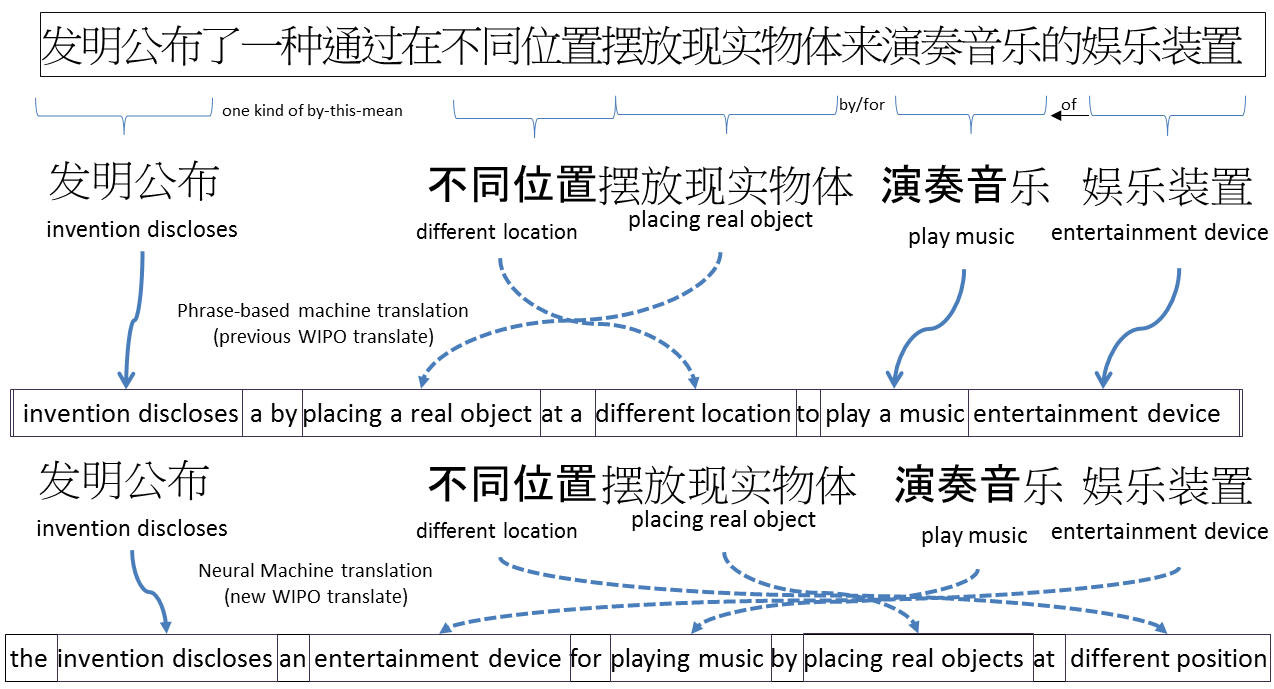
WIPO Translate now incorporates cutting-edge neural machine translation technology to render highly technical patent documents into a second language in a style and syntax that more closely mirrors common usage, out-performing other translation tools built on previous technologies.
WIPO has initially “trained” the new technology to translate Chinese, Japanese and Korean patent documents into English. Patent applications in those languages accounted for some 55% of worldwide filings in 20141. Users can already try out the Chinese-English translation facility on the public beta test platform.
“One of the aims of the patent system is to make technology available. Language is a barrier to the universal achievement of that aim. This breakthrough for WIPO Translate means that a vast, and ever-increasing, trove of patent documents will soon be more easily accessible to innovators who search these records for inspiration or technical know-how,” said WIPO Director General Francis Gurry. “As part of a global trend, patent applications are increasingly being filed in East Asian languages, particularly in Chinese, and WIPO Translate helps ensure that state-of-the-art knowledge created in these languages is shared as widely and rapidly as possible.”
Highly accurate
The high level of accuracy of the Chinese-English translation is the result of the training of the neural machine translation tool, which compared 60 million sentences from Chinese patent documents provided to WIPO’s PATENTSCOPE database by the State Intellectual Property Office of the People’s Republic of China with their translations as filed at the United States Patent and Trademark Office.
WIPO plans to extend the neural machine translation service to French-language patent applications, with other languages to follow. The PATENTSCOPE database integrates with other translation engines freely available on the internet and continues to use existing statistical-based translation technology for languages where it performs well. WIPO has shared its translation software with other international organizations, including the United Nations conference management service, Food and Agriculture Organization, International Telecommunication Union, International Maritime Organization, World Trade Organization, and The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. "At the United Nations, we are following with great interest the new developments on neural machine translation at WIPO, our partners in this innovative area,” said Cecilia Elizalde, Director of the UN Documentation Division. “Our translation system is integrated with the statistical version of WIPO Translate and translators find it very useful. We look forward to upgrading it to the neural version in the next months."
Emerging technology
Neural machine translation is an emerging technology. It is based on huge neural network models that “learn” from previously translated sentences. The specificity of neural machine translation (compared to previous “phrase based” statistical methods) is that it produces more natural word order, with particular improvements seen in so-called distant language pairs, like Japanese-English or Chinese-English.
In a recent test, WIPO Translate’s neural-based machine translation service substantially out-performed both the previous statistical-based model on distant language pairs, as well as other non-WIPO translation services. Since this WIPO tool is trained and focused uniquely on patent documents, instead of a more-disparate array of texts, it gives higher-quality renderings.
WIPO created its own software, based on open-source software and libraries (Nematus – Theano, AmuNMT), and capitalized on in-house expertise in handling large datasets.
Note to Editors:
The PATENTSCOPE database provides access to international Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) applications in full text format on the day of publication, as well as to patent documents of participating national and regional patent offices. The information may be searched by entering keywords, names of applicants, international patent classification and many other search criteria in multiple languages. The database contains some 58 million records.
About WIPO
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is the United Nations agency that serves the world’s innovators and creators, ensuring that their ideas travel safely to the market and improve lives everywhere.
We do so by providing services that enable creators, innovators and entrepreneurs to protect and promote their intellectual property (IP) across borders and acting as a forum for addressing cutting-edge IP issues. Our IP data and information guide decisionmakers the world over. And our impact-driven projects and technical assistance ensure IP benefits everyone, everywhere.
For more information, please contact the News and Media Division at WIPO:- Tel: (+41 22) 338 81 61 / 338 72 24